The Chip Crisis of 2025
The semiconductor industry is under intense pressure in 2025. Disruptions in global logistics, raw material shortages, and rising geopolitical tensions are testing the limits of a highly interdependent supply chain. As chip demand surges, addressing supply chain challenges in chip manufacturing has never been more critical. This guide explores key bottlenecks, strategic solutions, and the path forward for industry resilience.
Global Semiconductor Supply Chain: A Complex Web
Chip manufacturing relies on a globally dispersed, highly synchronized network:
- Raw Material Sourcing: Silicon from China, quartz from Brazil, and rare earths from Africa.
- Fabrication Hubs: Taiwan, South Korea, and the U.S.
- Assembly and Testing: Often in Southeast Asia (Malaysia, Vietnam)
- Distribution: Finished chips shipped globally for integration into everything from smartphones to satellites.
This intricate process leaves the semiconductor supply chain vulnerable to even small disruptions.
Key Chip Manufacturing Supply Chain Challenges
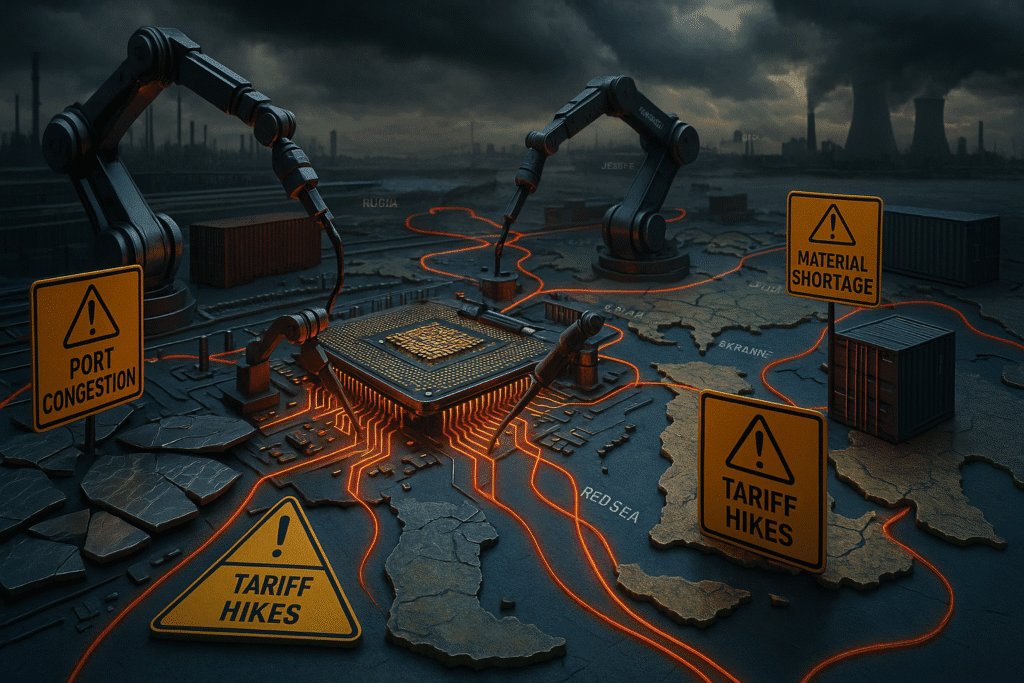
The most pressing issues include:
- Raw material shortages, especially silicon wafers and photoresists
- Overreliance on single-source suppliers for rare components
- Shipping & port congestion, worsened by the Russia-Ukraine and Red Sea crises
- Workforce gaps, particularly in skilled chip engineers
- Regulatory hurdles and rising tariffs affecting imports/exports
These challenges increase costs, delay chip deliveries, and stunt innovation.
Trade Policies and Their Impact on Semiconductor Flow
Global trade tensions—particularly U.S.–China dynamics—have:
- Raised semiconductor production costs via tariffs on critical components
- Limited access to chipmaking tools like EUV lithography machines
- Encouraged reshoring, but slowed cross-border chip collaboration
Solution: Pro-industry trade agreements, diplomatic tech pacts, and export-control transparency.
Material Shortages & Bottlenecks: Finding Alternatives
Critical inputs like copper foils, silicon carbide, and neon gas are running low. In response, companies are:
– Investing in material-efficient chip architectures
– Building long-term contracts with multiple global suppliers
– Developing alternative materials like graphene for next-gen chips
Predictive analytics and AI tools help forecast future shortages more accurately.
Geopolitical Risks: Mitigating Political Volatility
With chip tech becoming geopolitically sensitive, disruptions come from:
- Sanctions and export controls
- Nationalistic resource hoarding
- Conflicts disrupting shipping lanes
Strategic Steps:
- Geopolitical risk mapping
- Multi-region supplier diversification
- Policy lobbying via international chip alliances
Transportation & Labor: Logistics Meet Human Capital
Logistical Challenges:
- Port delays and warehousing backlogs
- Rising air cargo costs
Labour Constraints:
- Shortage of semiconductor engineers
- High turnover in fab facilities
Fixes:
- Smart logistics platforms using IoT for real-time tracking
- Cross-border engineering training programs
- Robotics and automation in assembly lines
Building Supply Chain Resilience: Core Strategies
To stabilize operations, chip manufacturers are adopting:
- Supplier diversification and region-specific sourcing
- Smart inventory management via digital twins
- AI-based demand forecasting to buffer fluctuations
These strategies prevent future stockouts and production halts.
Reshoring, Nearshoring & Diversification: A Global Realignment
Bringing chip production closer to home:
- Reshoring (to U.S., EU, India) ensures IP safety & reliability
- Nearshoring (to Mexico, Eastern Europe) optimizes cost & speed
- Multi-site fabrication reduces region-specific risks
Governments are incentivizing local fabs to ensure chip sovereignty.
Digital Supply Chains: Smarter, Faster, More Predictive
Tech-led transformation includes:
- Blockchain for transparency
- AI & ML for real-time demand insights
- Cloud ERP for integrated production tracking
This digital backbone makes the supply chain more responsive, agile, and secure.
Industry-Government Synergy: Policy-Backed Stability
Policy Recommendations:
- Tax credits for domestic chip investment
- Open-data collaboration platforms
- Funding for chip workforce education
Examples: CHIPS Act (U.S.), Digital India Semiconductor Mission, EU Chips Act, USA-India partnership to explore semicondutor supply chain opportunities.
Future Outlook: A Smarter, More Self-Reliant Ecosystem
Looking ahead:
- AI, EVs, IoT, Green Energy Sector will multiply chip demand
- Risks from climate, cybercrime, and geopolitics will persist
Winning Formula: Resilient supply chains + digital tools + global alliances.
Action Items for Stakeholders
To thrive in 2025 and beyond:
- Diversify supply lines and automate logistics
- Adopt predictive data tools and talent retention strategies
- Engage policymakers for long-term stability
The semiconductor industry must shift from reactive crisis management to proactive resilience building. The time to future-proof chip supply chains is now.
🔑 Key Takeaways:
- Chip supply chains are facing unprecedented strain in 2025
- Raw material access, trade wars, and labour gaps are critical
- Solutions lie in digital tools, global alliances, and regional diversification
Summary
The global semiconductor industry is facing significant Chip Manufacturing Supply Chain Challenges in 2025. Key issues include rising factory infrastructure costs, geopolitical tensions, talent shortages, and limited access to essential raw materials like silicon wafers and rare earth elements. These factors, combined with surging demand from AI and cloud computing sectors, are straining supply chains, causing longer lead times and higher prices. Companies are responding by diversifying suppliers and investing in new production techniques, but the risk of renewed shortages remains high