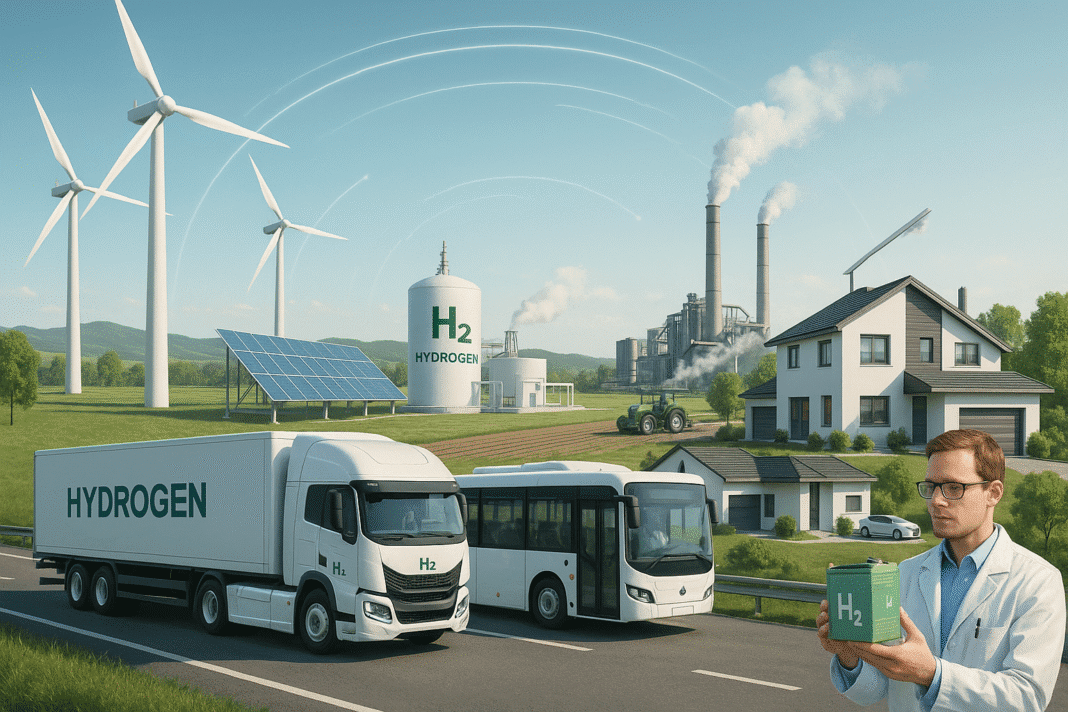
Green-hydrogen is emerging as a pivotal player in the quest for sustainable energy. It is produced through electrolysis, a process that uses renewable electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This method results in zero carbon emissions, making it a clean energy source.
The primary sources of renewable electricity for this process are solar, wind, and hydropower. These sources ensure that green-hydrogen remains a truly sustainable option. As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, green-hydrogen offers a promising solution.
Hydrogen fuel cells, which convert hydrogen into electricity, emit only water vapor. This makes them an attractive alternative to fossil fuels. Green-hydrogen can be used in various sectors, including transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
Countries around the globe are investing in green-hydrogen infrastructure. Nations like Germany, Japan, and Australia are leading the charge. However, challenges such as high production costs and technological hurdles remain.
Despite these challenges, the potential of green-hydrogen is immense. It can help decarbonize sectors that are difficult to electrify. As research and innovation continue, green-hydrogen is poised to play a crucial role in the energy transition.
What is Green-Hydrogen?
Green-hydrogen is a clean form of hydrogen produced using renewable energy sources. It stands out due to its environmentally friendly production process. Unlike other hydrogen types, it generates no carbon emissions during its creation.
The production involves a technique known as electrolysis. This process uses electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. By using renewable electricity from solar panels, wind turbines, or hydropower stations, the entire cycle is sustainable.
Green-hydrogen is distinct from other hydrogen types, such as blue and grey. While blue hydrogen is derived from fossil fuels and employs carbon capture and storage, grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas without capturing emissions. Thus, green-hydrogen is the most eco-friendly option.
Its versatility is appealing across various sectors, such as transportation and industry. Here are some key features:
- Renewable Source: Produced using 100% renewable energy.
- Emission-Free: No carbon emissions in the production process.
- Flexible Use: Applicable in diverse industries and technologies.
This clean energy source holds promise for future energy needs. As technology improves and costs decrease, green hydrogen could become a cornerstone of the global energy landscape. The focus on sustainability and reducing carbon footprints enhances its relevance in today’s world.
The Science Behind Green-Hydrogen Production
The production of green-hydrogen hinges on a process called electrolysis. This scientific method utilizes electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. What sets it apart is its reliance on renewable energy sources, ensuring an emission-free process.
In electrolysis, water molecules are separated in an electrolyzer. This device channels electricity to trigger the separation. The most common type of electrolyzer used is the proton exchange membrane (PEM). This membrane facilitates the efficient passage of protons while maintaining high purity levels in the hydrogen.
Renewable energy powers electrolysis. Solar panels capture sunlight, wind turbines harness breezes, and hydropower exploits water flow to produce electricity. This synergy ensures that the hydrogen generated is genuinely “green.”
A few remarkable aspects of electrolysis include:
- Efficiency: Modern technologies achieve remarkable energy conversion rates, optimizing resource use.
- Scalability: Electrolysis can scale to meet rising demand, from small to large installations.
- Purity: The hydrogen obtained is of high purity, suitable for sensitive applications.
The entire process culminates in harvesting hydrogen gas, a versatile energy carrier. This environmentally benign output makes it perfect for countless applications while aligning with global sustainability goals.
Continued research is advancing the field of electrolysis. Innovative materials and processes are emerging to boost efficiency further and reduce costs. As these scientific advances unfold, green-hydrogen’s role in global energy systems grows more prominent. This underscores its potential to revolutionize energy production, ushering in a more sustainable future.
Comparing Hydrogen Types: Green, Blue, and Grey
Hydrogen can be produced through various methods, resulting in different types, namely green, blue, and grey hydrogen. These types differ mainly based on their production processes and their environmental impacts. This distinction is crucial for understanding hydrogen’s role in sustainable energy solutions.
Green-hydrogen is the most eco-friendly type. Produced via electrolysis using renewable electricity, it boasts zero carbon emissions. This makes it a cornerstone in efforts to transition to cleaner energy systems. Blue hydrogen is somewhat of a bridge between green and grey. It is derived from natural gas through a process that captures and stores carbon emissions, keeping their impact lower than grey hydrogen. Grey hydrogen, the most common form, is also produced from natural gas but without capturing emissions, resulting in a significant carbon footprint.
Here’s a quick rundown of these hydrogen types:
- Green-Hydrogen: Produced using renewable energy, carbon-free.
- Blue Hydrogen: Low-emissions production with carbon capture.
- Grey Hydrogen: Emission-heavy, non-renewable production process.
Understanding these differences helps in assessing their roles in transitioning to a low-carbon economy. The choice of hydrogen type impacts environmental strategies, economic viability, and technology development in various industries. As the world pushes towards sustainability, green hydrogen stands out as the future of clean energy.
Applications of Green-Hydrogen in Modern Society
Green-hydrogen is revolutionizing various sectors with its broad applications, playing a crucial role in modern society. One significant use is in the transportation industry. Hydrogen fuel cells are an emerging clean alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, especially in heavy-duty vehicles such as buses and trucks.
In power generation, green-hydrogen provides a sustainable solution to stabilize energy supplies. By storing surplus energy generated from renewables like solar and wind, it ensures a continuous energy supply even when these sources are not actively producing power. This adaptability makes it essential for integrating renewable energy into national grids.
Moreover, green hydrogen finds applications in industrial processes. Industries such as steelmaking and chemical production are turning to hydrogen to reduce their carbon emissions. By replacing fossil fuels with green-hydrogen, these industries can significantly lower their environmental impact.
Here’s a list of key applications of green-hydrogen:
- Transportation: Fuel cells in vehicles.
- Power generation: Energy storage and supply.
- Industrial use: Decarbonizing heavy industries.
In the field of residential energy, hydrogen can be used for heating and cooking. This application has the potential to reduce household reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon footprints. Additionally, hydrogen is being explored in agriculture to power machinery and as a potential fertilizer component, boosting sustainable practices.
The diverse applications of green hydrogen highlight its importance in creating a sustainable future. As technology advances, the scope of these applications is expected to expand, offering even more solutions to modern challenges.
Green-Hydrogen and the Energy Transition
Green hydrogen is a pivotal element in the global energy transition. Its potential to replace fossil fuels helps achieve a low-carbon economy. By utilizing renewable resources for its production, it significantly reduces carbon emissions.
Energy transition involves shifting from traditional energy sources like oil and coal to renewable and cleaner alternatives. Green-hydrogen supports this shift by providing clean energy storage solutions and powering diverse sectors. It complements renewable energy sources such as wind and solar by storing excess energy and ensuring a steady supply.
Adopting green hydrogen could transform the energy landscape, encouraging sustainable practices worldwide. It offers a flexible solution that spans across various industries, promising to meet different energy needs. Countries investing in green hydrogen are leading the charge toward a cleaner future.
Key roles of green hydrogen in the energy transition include:
- Decarbonizing industries: Replacing fossil fuels in hard-to-electrify sectors.
- Energy storage: Balancing supply and demand with renewable energy sources.
- Integrating renewables: Supporting grid stability and energy resilience.
Through policy support and technology advancements, green hydrogen is becoming more accessible and cost-effective. It fosters an energy system that is not only sustainable but also resilient to climate impacts. As we strive for a greener economy, green hydrogen stands at the forefront, paving the way for long-lasting environmental benefits.
Challenges and Barriers to Widespread Adoption
Green-hydrogen holds great promise, but several challenges impede its widespread adoption. High production costs remain a significant hurdle. Electrolysis, the technology for producing green hydrogen, requires expensive materials and infrastructure. These costs make it less competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
Another barrier is the need for technological improvements. Current electrolysis methods lack efficiency, which raises energy requirements. Continual research and development are needed to enhance the efficiency and reduce the costs of hydrogen production.
Infrastructure for distribution and storage is also limited. Developing a network to transport hydrogen safely and effectively is crucial. Currently, the lack of refueling stations and pipelines limits its use in transportation and industry. Rapidly developing economy like India has developed a special purpose vehicle National Green Hydrogen-Mission.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks and policy support vary worldwide. Clear policies and incentives are necessary to encourage investment in green hydrogen technologies. Without consistent policies, market growth can be inconsistent and fragmented.
Major barriers include:
- Cost factors: High cost of production and infrastructure.
- Technological constraints: Limited efficiency and capacity of current systems.
- Infrastructure limitations: Inadequate distribution and storage networks.
- Policy inconsistencies: Need for international collaboration on regulations.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of green hydrogen justify efforts to overcome these barriers. By addressing these issues, green hydrogen can become an integral part of sustainable energy systems globally.
Innovations and Research in Green Hydrogen Technologies
Innovation in green-hydrogen technology is rapidly advancing. Research focuses on improving electrolysis efficiency and reducing costs. Enhanced catalysts are a key area of development. These catalysts accelerate reactions, making hydrogen production more economical.
Storage methods are also progressing. Scientists are exploring metal hydrides and liquid organic hydrogen carriers. These alternatives offer safer and more efficient storage solutions. Advances in these areas could transform how hydrogen is stored and transported.
Transportation infrastructure is being innovated. New pipeline materials and designs aim to enhance hydrogen’s safe movement. Furthermore, novel fueling station technologies are emerging, making hydrogen more accessible for vehicles.
Research and innovations in green hydrogen include:
- Catalyst advancements: Development of cost-effective, efficient catalysts.
- Storage solutions: Exploration of metal hydrides and organic carriers.
- Pipeline technology: New materials for safe, efficient transport.
- Fueling stations: Improved accessibility and refueling technologies.
Continued investment in research is essential. Governments, industries, and academic institutions are collaborating worldwide. Such partnerships accelerate technological breakthroughs. They ensure that green hydrogen becomes a viable and critical component of sustainable energy systems globally. The future of green hydrogen depends on overcoming current technological challenges and unlocking its full potential.
Global Initiatives and Policy Support
Countries around the world are recognizing the potential of green hydrogen. Governments are implementing policies to promote its development. Many nations have set ambitious hydrogen production targets. These targets are part of wider plans to reduce carbon emissions.
International cooperation is key. Global initiatives are facilitating cross-border collaboration. These initiatives aim to establish standardized regulations and technical benchmarks. Harmonized standards are crucial for widespread adoption.
Several countries are leading by example with robust policies. Noteworthy efforts include:
- Germany: Investment in hydrogen infrastructure and technology.
- Japan: Support for research and commercial applications.
- Australia: Renewable energy exports using hydrogen.
Policy support plays a vital role in green hydrogen’s growth. Incentives like tax breaks and subsidies encourage research and development. This financial backing is crucial for overcoming economic barriers. It helps lower costs, making hydrogen more competitive.
Ultimately, global commitment and collaborative efforts will drive green hydrogen’s integration into energy systems. This will help pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future. The continued alignment of policies and initiatives is essential to support this transition effectively.
The Future of Green Hydrogen: Opportunities and Outlook
The future of green hydrogen shines with promise and potential. As global interest intensifies, investment in hydrogen technologies is increasing. Nations prioritize it as a core component of climate strategies. This will drive significant advancements in production and usage.
Key opportunities for green hydrogen are emerging in various sectors. Heavy industries and aviation are exploring its benefits. These sectors are hard to electrify, making hydrogen a viable alternative. Transportation and power generation also see potential in green hydrogen applications.
Several factors are expected to influence green hydrogen’s outlook:
- Technological Breakthroughs: Innovations in electrolysis to improve efficiency.
- Economic Shifts: Lowering costs of renewable electricity and electrolyzer technologies.
- Collaborative Efforts: Joint ventures and partnerships between countries and industries.
However, challenges remain, requiring concerted action. Overcoming high production costs is essential for scaling up. Furthermore, infrastructure development and policy frameworks need advancement. Such enhancements will facilitate a seamless integration of hydrogen into energy systems.
In conclusion, the path ahead for green hydrogen involves balancing opportunities with obstacles. Strategic investments and innovation are vital to unlock its full potential. Green hydrogen stands at the forefront of a sustainable and resilient energy future. Leveraging its benefits will require concerted efforts globally.
Conclusion: The Role of Green Hydrogen in a Sustainable World
Green hydrogen is pivotal in crafting a sustainable future. By harnessing renewable resources, it offers clean energy solutions. Its impact can transform energy consumption across industries and sectors. When humans society are witnessing change in the lifestyle for greener tomorrow, addition if green hydrogen as energy option will definitely boost the sustainable living goals. As societies shift toward greener lifestyles, the integration of green hydrogen as an energy source will significantly advance sustainable living goals.
As we seek to curb carbon emissions, green hydrogen provides an adaptable alternative. Key to achieving climate goals, it fosters innovation and economic opportunities. With ongoing research and development, green hydrogen stands to reshape energy landscapes. Collaboration and policy support will bolster its role in a sustainable world, ensuring a cleaner, greener future for all.