India’s Universal Immunization Programme (UIP) has expanded from 6 vaccines in 2013 to 12 vaccines in 2024, including:
- Rotavirus Vaccine
- Inactivated Polio-virus Vaccine
- Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine
- Measles-Rubella Vaccine
- Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine (adult)
- Tetanus-Diphtheria (Td) Vaccine
The UIP provides free immunization to 2.6 crore infants and 2.9 crore pregnant women annually through over 1.3 crore sessions.
Mission Indradhanush & Zero Dose Implementation Plan 2024
India has launched focused campaigns to cover unvaccinated populations:
- Mission Indradhanush (since 2014): Vaccinated 5.46 crore children and 1.32 crore pregnant women
- Zero Dose Implementation Plan 2024: Rolled out across 143 districts in 11 high-burden states
- Pulse Polio Campaigns: Maintained India’s polio-free status since 2014
Technology and Community-Driven Immunization
India’s tech-driven strategy includes:
- U-WIN Platform: Digitally tracks immunization to prevent dropouts
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Mass media, community radio, social media, and street plays
- Healthcare Worker Network: ASHAs and ANMs go door-to-door for immunization and education
Global Comparisons: India Outperforms in Antigen Coverage
India’s antigen-wise vaccine coverage surpasses global averages:
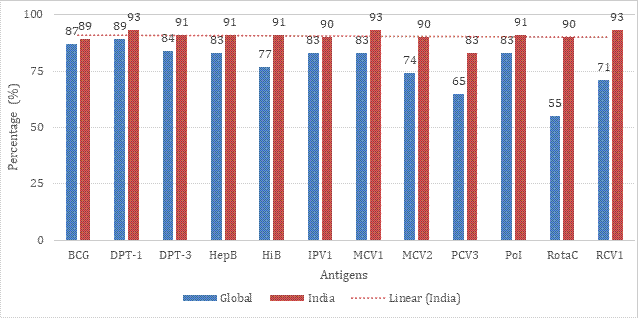
Antigen wise comparison between India and Global coverage (%)
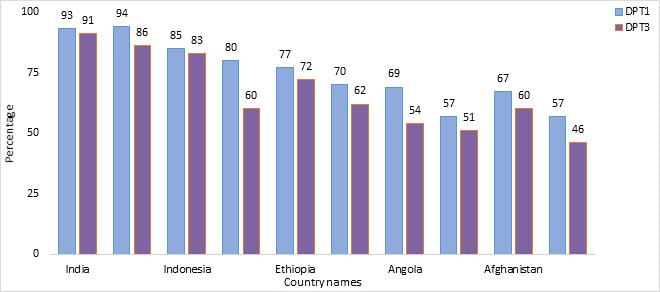
Comparison between India and 9 Countries with high number of zero dose children for DTP 1 & 3 (%) (WUENIC 2023)
- DTP-1 coverage at 93% vs. Nigeria’s 70%
- Measles vaccine coverage increased from 83% (2013) to 93% (2023)
- Dropout rate from DTP-1 to DTP-3 reduced from 7% (2013) to 2% (2023)
Source: WHO/UNICEF Estimates of National Immunization Coverage (WUENIC) 2023
Why India Stands Apart
Despite its massive population, India performs on par or better than high-income countries like:
- New Zealand (DTP-1: 93%)
- Germany, Finland (DTP-3: 91%)
- Sweden (MCV-1: 93%)
- Ireland (PCV-3: 83%)
In contrast, high zero-dose burden countries such as Yemen (1.68%) and Nigeria (0.98%) show significantly higher proportions compared to India’s 0.06% in 2024.
Global Recognition
India was awarded the Measles and Rubella Champion Award 2024 by the Measles & Rubella Partnership (UNICEF, WHO, BMGF, GAVI, CDC, etc.) in Washington DC, recognizing its exemplary efforts in child immunization.
Sustainable Immunization Strategy: India’s Long-Term Vision
India’s focus on last-mile vaccine delivery, particularly in underserved and hard-to-reach populations, is the cornerstone of its strategy:
- Village Health & Nutrition Days (VHNDs)
- Multi-tiered Task Forces (STFI, DTFI, BTFI)
- Doorstep Immunization with awareness-building
From Polio elimination (2014) to Tetanus eradication (2015), and now Measles-Rubella elimination (2025 campaign), India continues to lead through innovation, collaboration, and execution.
India’s achievements in immunization are not just numbers—they’re lives saved, futures secured, and global benchmarks set. With sustained political will, technological innovation, and community engagement, India is not just catching up—it is leading the world in child and maternal health.




